Gas Exchange Respiratory System. This review provides an overview of the relationship between ventilationperfusion ratios and gas exchange in the lung emphasising basic concepts and relating them to clinical scenarios. For each gas exchanging unit the alveolar and effluent blood partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide P O2 and P CO2 are determined by the ratio of alveolar ventilation to blood flow V A.
For each gas exchanging unit the alveolar and effluent blood partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide P O2 and P CO2 are determined by the ratio of alveolar ventilation to blood flow V A. This review provides an overview of the relationship between ventilationperfusion ratios and gas exchange in the lung emphasising basic concepts and relating them to clinical scenarios. Air enters the respiratory systems of insects through a series of external openings called spiraclesThese external openings which act as muscular valves in some insects lead to the internal respiratory system a densely networked array of.
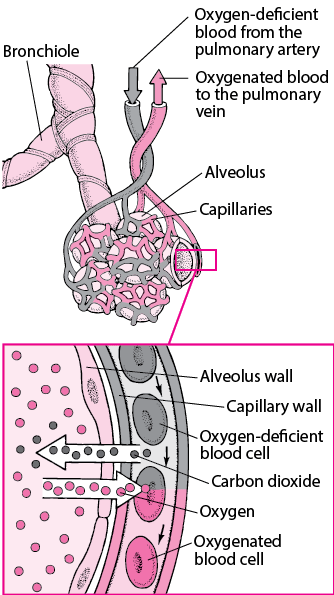
Lower respiratory system Larynx trachea bronchi and lungs Functionally Conducting zone conducts air to lungs Nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi bronchioles and terminal bronchioles Respiratory zone main site of gas exchange Respiratory bronchioles alveolar ducts alveolar sacs and alveoli.
This review provides an overview of the relationship between ventilationperfusion ratios and gas exchange in the lung emphasising basic concepts and relating them to clinical scenarios. Carbohydrate or fat is being metabolized to supply the body. System is partitioned homogeneously so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. For each gas exchanging unit the alveolar and effluent blood partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide P O2 and P CO2 are determined by the ratio of alveolar ventilation to blood flow V A.
