Floor Of Anatomy Bone. The pelvic bones are. Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD PhD Last reviewed.
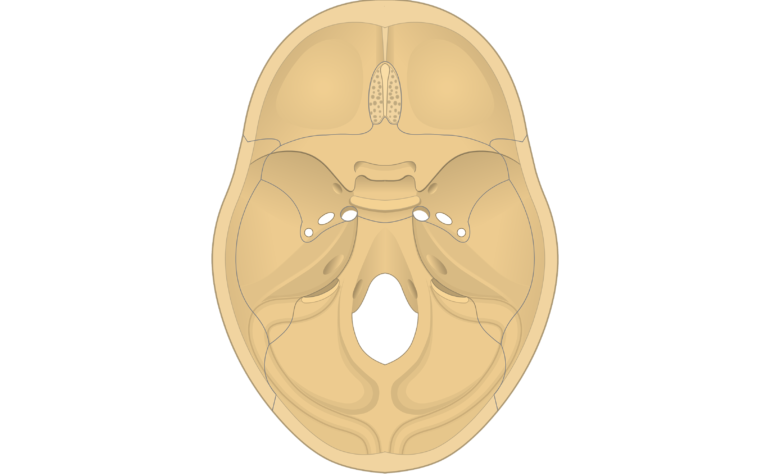
The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that make up the orbit the space that holds the eyeball and helps make up the floor of the middle cranial fossa the butterfly-shaped depression at the base of the skull that houses the temporal lobes of the cerebellum. Quizzes on human skeletal system anatomy bone anatomy and bone markings. The middle ear is an air-filled cavity within the petrous portion of the temporal bone that contains the ossicular chain and is bounded by the tympanic membrane laterally the inner ear structures surrounded by the otic capsule and the cochlear promontory medially the tegmen tympani superiorly and the jugular wall floor inferiorly.
Quizzes on human skeletal system anatomy bone anatomy and bone markings.
Cancellous bone also called trabecular or spongy bone is the internal tissue of the skeletal bone and is an open cell porous network. The medial floor is primarily formed by the maxilla with a small contribution from the palatine bone. Anatomy of the Hyoid The hyoid is situated at the front or anterior part of the neck between the jaw bone and the thyroid cartilage and is firmly secured to the thyroid cartilage by ligaments. It resides at the level of the third cervical vertebra attaching indirectly by means of tendons to muscles of the tongue the floor of the mouth and the anterior neck.
